Summary
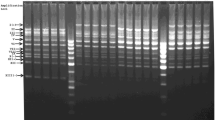
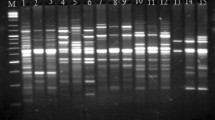
We tested the applicability of the random amplified polymorphic deoxyribonucleic acid (RAPD) analysis for identification of three marine fish cell lines FG, SPH, and RSBF, and as a possible tool to detect cross-contamination. Sixty commercial 10-mer RAPD primers were tested on the cell lines and on samples collected from individual fish. The results obtained showed that the cell lines could be identified to the correspondent species on the basis of identical patterns produced by 35–48% of the primers tested; the total mean similarity indices for cell lines versus correspondent species of individual fish ranged from 0.825 to 0.851, indicating the existence of genetic variation in these cell lines in relation to the species of their origin. Also, four primers, which gave a monomorphic band pattern within species/line, but different among the species/line, were obtained. These primers can be useful for identification of these cell lines and for characterization of the genetic variation of these cell lines in relation to the species of their origin. This supported the use of RAPD analysis as an effective tool in species identification and cross-contamination test among different cell lines.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bardakci, F.; Skibinski, D. O. F. Application of the RAPD technique in tilapia fish: species and subspecies identification. Heredity 73:117–123; 1994.
Cocconcelli, P. S.; Porro, D.; Galandini, S.; Senini, L. Development of RAPD protocol for typing of strains of lactic acid bacteria and enterococci. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 21:376–379; 1995.
Ferrero, M.; Castano, A.; Gonzalez, A.; Sanz, F.; Becerril, C. Characterization of RTG-2 fish cell line by randomly amplified polymorphic DNA. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety 40:56–64; 1998.
Freshney, R. I. Culture of animal cells, a manual of basic technique. 2nd ed. New York: Alan R. Liss; 1987.
Fryer, J. L.; Lannan, G. N. Three decades of fish cell culture: a current listing of cell lines. J. Tissue Cult. Methods 16(2):87–94; 1994.
Kawai, Y.; Mitsuhashi, J. An insect cell line discrimination method by RAPD-PCR. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 33A:512–515; 1997.
Keshava, C.; Keshava, N.; Zhou, G.; Whong, W. Z.; Ong, T. M. Genetic instability in silica- and cadmium chloride-transformed BALB/c-3T3 and tumor cell lines by randomly amplified polymorphic DNA analysis. Mutat. Res. 425:117–123; 1999.
Koh, T. L.; Khoo, G.; Fan, L. Q.; Phang, V. P. E. Genetic diversity among wild forms and cultivated varieties of discus (Symphysodon spp.) as revealed by randomly amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) fingerprinting. Aquaculture 173:485–497; 1999.
Li, Y. N.; Mao, S. J.; Zhang, Y. Establishment of two newly developed cell strains from caudal fin tissue of grass carp (HGC-87) and gill cover membrane tissue of crucian carp (HCC-87). In: Mao, S. J., ed. Monograph of life sciences. Hangzhou: Hangzhou University Press; 1992:114–119.
Liu, Z. J.; Li, P.; Argue, B. J.; Dunham, R. A. Randomly amplified polymorphic DNA markers: usefulness for gene mapping and analysis of genetic variation of catfish. Aquaculture 174:59–68; 1999.
Nei, M.; Li, W. H. Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 76:5269–5273; 1979.
Sambrook, J.; Fritsch, E. F.; Maniatis, T. Molecular cloning—a laboratory manual. 2nd ed. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1989.
Tong, S. L.; Li, H.; Miao, H. Z. The establishment and partial characterization of a continuous fish cell line FG-9307 from the gill of flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Aquaculture 156:327–333; 1997.
Tong, S. L.; Miao, H. Z.; Li, H. Three new continuous fish cell lines of SPH, SPS and RSBF derived from sea perch (Lateolabrax japonicus) and red sea bream (Pagrosomus major). Aquaculture 169:143–151; 1998.
Welsh, J.; McClelland, M. Fingerprinting genomes using PCR with arbitrary primers. Nucleic-Acids Res. 18(24):7213–7218; 1990.
Williams, J. G. K.; Kubelik, A. R.; Livak, K. J.; Rafalski, J. A.; Tingey, S. V. DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic-Acids Res. 18(22):6531–6535; 1990.
Wolf, K.; Quimby, M. C. Established eurythermic line of fish cells in vitro. Science 135:1065–1066; 1962.
Zhang, N. C.; Yang, G. Z. The establishment of strain ZC-9701 and substrain ZC-9701 S1 from the snout tissue cells of grass carp. Acta Biol. Exp. Sin. 14:101–105; 1981.
Zuo, W. G.; Qian, H. X.; Xu, Y. F.; Du, S. Y.; Yang, X. L. A cell line derived from the kidney of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus). J. Fish. China 10:11–17; 1996.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, HR., Zhang, SC., Tong, SL. et al. Analysis of three marine fish cell lines by RAPD assay. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 37, 430–433 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1290/1071-2690(2001)037<0430:AOTMFC>2.0.CO;2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1290/1071-2690(2001)037<0430:AOTMFC>2.0.CO;2